A New Horizon in Commercial Construction: Geothermal Heating and Cooling
In the rush to find non-carbon energy sources for buildings, one alternative is gaining notable traction: geothermal heating and cooling systems. These systems are already being used effectively in residential and commercial structures. And with strong government support, their use is bound to increase, because they offer a number of benefits and advantages over conventional HVAC systems, including:
-
No fuel consumption (beyond what is needed to power some electrical components).
-
No carbon emissions.
-
No need to connect to public utilities.
-
Relatively low cost.
-
Low maintenance requirements.
-
Ability to provide both heat and cooling from one system.
Geothermal heating and cooling systems (not to be confused with geothermal power plants, which use the heat from steam wells or hot water wells to produce electrical energy) simply transfer heat or cold from underground to the surface to achieve desired temperature levels in a structure.
Here’s how it works:
Our air typically gets cold in the winter and hot in the summer. But just a few feet below the surface of the ground, temperatures stay remarkably constant year-round—between 50 and 59 degrees Fahrenheit. Geothermal heating and cooling systems take advantage of this, using the stable temperatures in the ground to provide cooling during the summer and heat in the winter. They can serve, alternately, as a heat sink and a heat source.
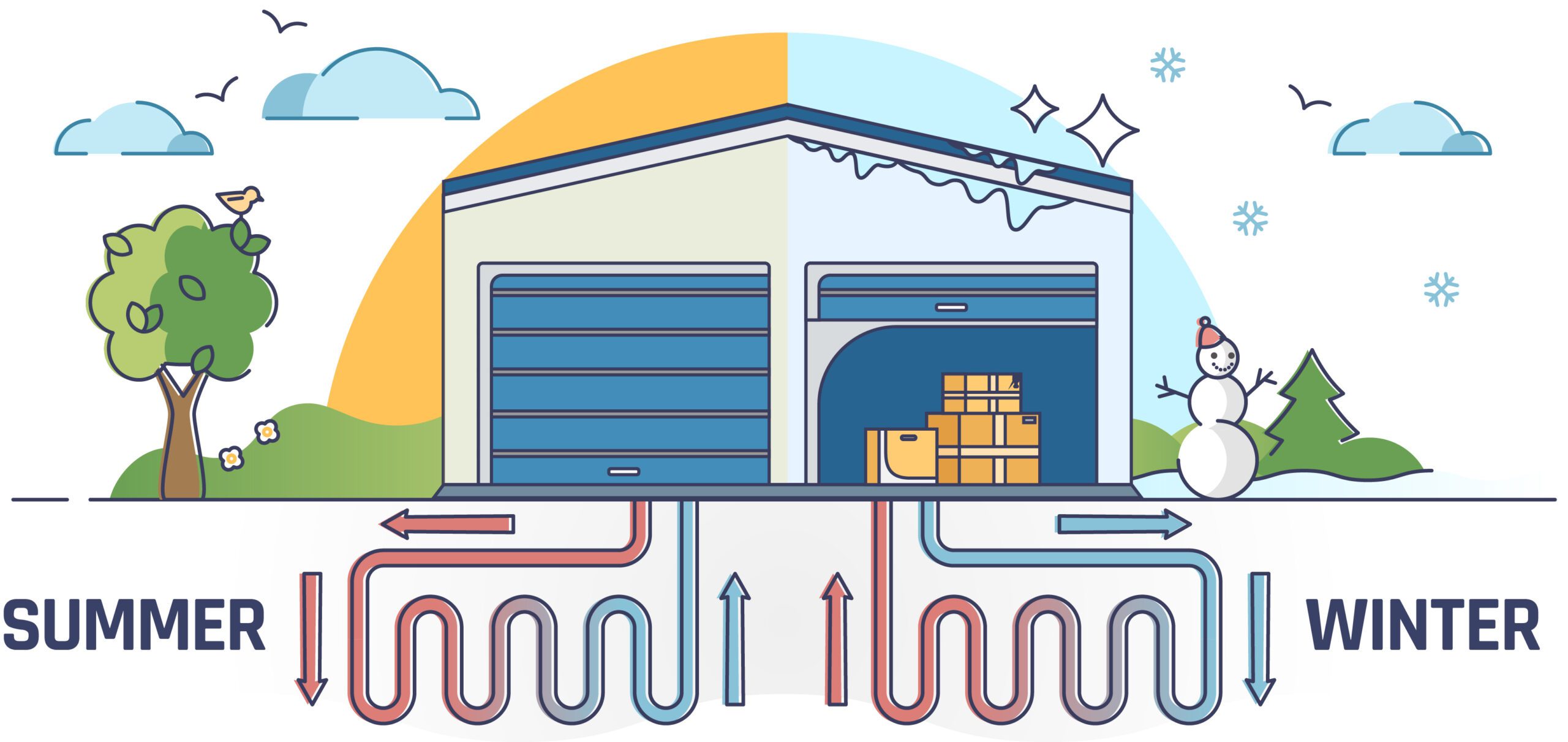
A geothermal heat pump circulates fluid through a ground loop—a pipe system that extends underground. The fluid, typically made up of water mixed with antifreeze, passes through the pipes and absorbs the temperature of the surrounding ground. It ascends back to the heat pump and disseminates the moderated temperature into the structure through a duct system.
Ground loops can extend horizontally a few feet below the surface or go as deep as 500 feet down in a vertical system. (The latter option is especially practical when the square footage of the land parcel is small.)
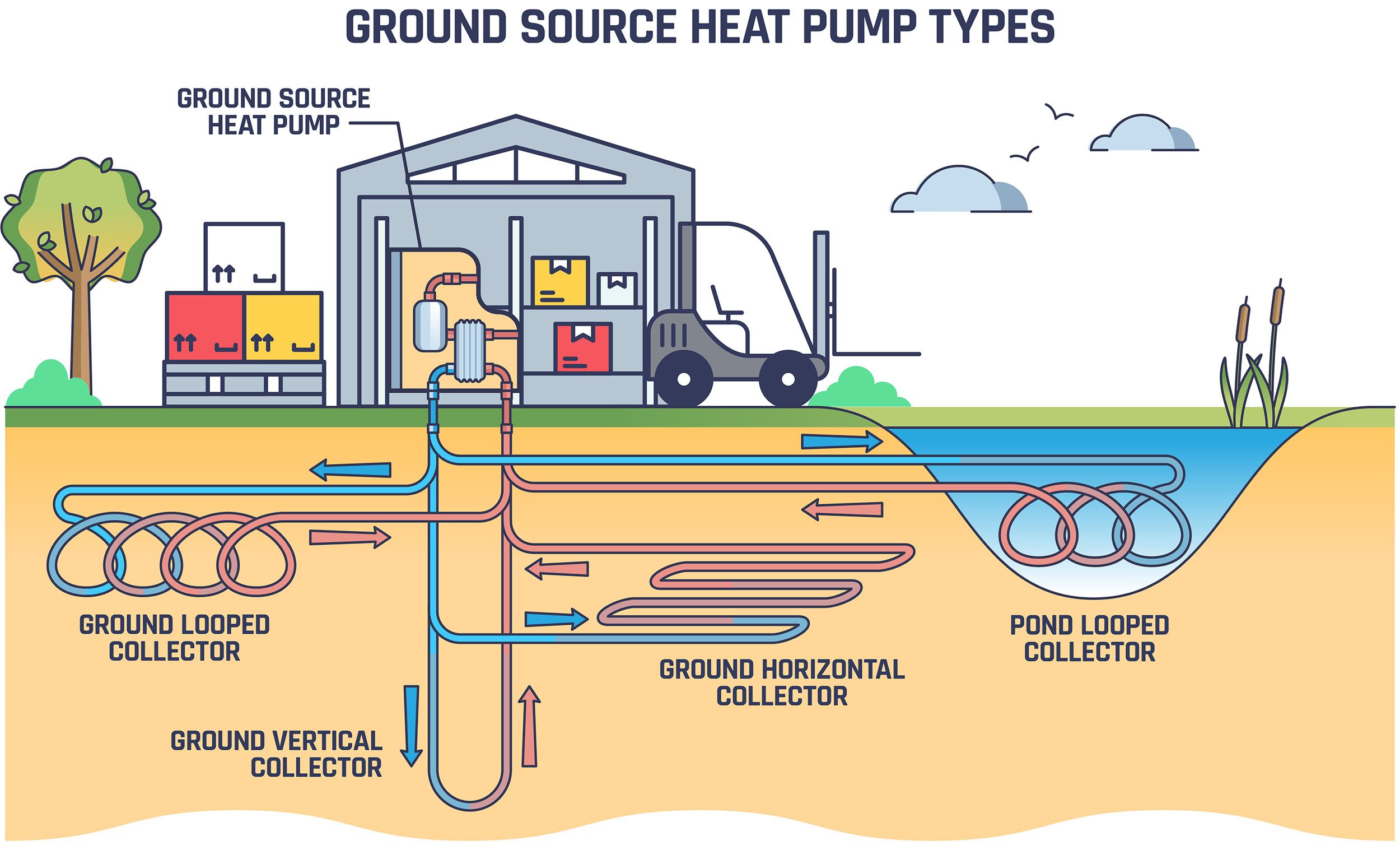
Geothermal Heating and Cooling in Commercial Construction
The advantages of geothermal systems for residential construction are clear. And there are now more than a million such systems installed in American homes. Those same advantages apply on a larger scale for commercial and industrial structures.
With the government’s emphasis on energy efficiency, geothermal systems have received special attention. Facilities in a dozen federal agencies now use geothermal HVAC systems. And through 2032, private construction projects can qualify for a 30% tax credit for ENERGY STAR-rated geothermal systems as well as an Investment Tax Credit.
It is now possible to meet the HVAC needs of entire communities with geothermal systems. In 2022, the U.S. Department of Energy, through its Geothermal Technologies Office, created a Community Geothermal Heating and Cooling Design and Deployment program, with $13 million allocated to support qualified projects that employ geothermal systems on a community level. So far, 11 projects have been selected for the program, with more to be included in phase two.
What About Retrofitting?
Geothermal heating and cooling systems clearly make sense for new construction. But they can also be retrofitted for existing structures. The conventional HVAC compressor and furnace are typically replaced with the geothermal heat pump and other equipment. But the new system can usually use the existing ducting.
A feasibility study is essential in determining the effectiveness of this option, especially for existing structures. The U.S. Department of Energy has been known to help with this endeavor.

Geothermal Heating and Cooling: A Promising Frontier
Beyond the benefits already mentioned, geothermal systems:
-
Are virtually noise-free.
-
Are safe, without flames or fumes from energy combustion.
-
Last an average of 20 to 25 years (compared with 15 to 20 years for conventional systems).
-
Can save commercial buildings up to 44% on heating costs and up to 48% on cooling costs.
-
Require relatively little maintenance.
-
Can enhance a company’s brand image and property value.
In addition to federal incentives, individual states have programs that can support investment in geothermal systems. The possibilities of this technology to drastically reduce carbon emissions, costs, and strains on the electrical grid have captured the attention of policymakers and thought leaders in the US and around the world.
And the potential has barely been tapped.



